NAT (Network Address Translation) is a process of changing the source and destination IP addresses and ports. Address translation reduces the need for IPv4 public addresses and hides private network address ranges. The process is usually done by routers or firewalls.
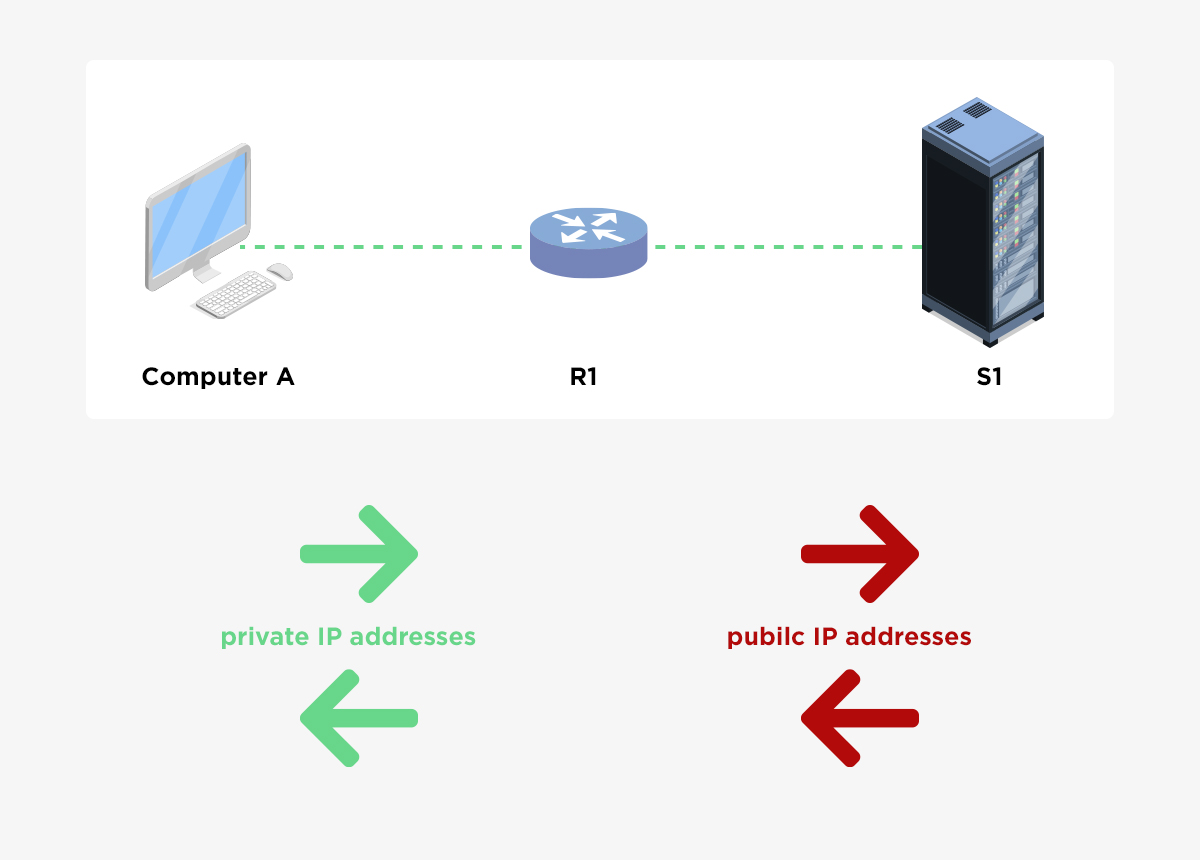
NAT allows a single device, such as a router, to act as an agent between the Internet (or public network) and a local network (or private network), which means that only a single unique IP address is required to represent an entire group of computers to anything outside their network.